
Figure 1: AI systems assisting healthcare professionals in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning
Introduction: Why This Matters
The integration of AI in healthcare represents one of the most significant transformations in the history of medicine. We are witnessing a paradigm shift from traditional healthcare delivery to intelligent, data-driven medical practices that promise to save lives, reduce costs, and make quality healthcare accessible to millions. The application of artificial intelligence healthcare solutions is not just enhancing existing medical practices—it’s fundamentally redefining what’s possible in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
Consider this: AI systems can now analyze medical images with accuracy rates that rival experienced radiologists, predict disease outbreaks before they happen, and personalize treatment plans based on individual genetic makeup. The global market for AI in healthcare is projected to reach $188 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 48% from 2022 to 2030. This explosive growth underscores the transformative potential of AI technologies in addressing some of healthcare’s most pressing challenges.
This comprehensive guide explores how AI in healthcare is revolutionizing medical practices, improving patient outcomes, and creating new possibilities for healthcare delivery. Understanding this transformation is crucial for healthcare professionals, patients, policymakers, and anyone interested in the future of medicine.
Part 1: Background and Context – The Evolution of Medical Technology
The journey toward AI in healthcare has been decades in the making, evolving through several distinct technological eras:
The Analog Era (Pre-1980s)
Healthcare relied on manual record-keeping, physical examinations, and basic diagnostic tools. Medical knowledge was largely experiential, and treatment decisions were based on generalized protocols rather than personalized data.
The Digitalization Wave (1980s-2000s)
The introduction of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and digital imaging systems marked the beginning of healthcare’s digital transformation. This era saw the standardization of medical data but struggled with interoperability and data silos.
The Connected Health Era (2000-2015)
The rise of telemedicine, wearable devices, and health apps created new possibilities for remote monitoring and patient engagement. However, these systems often operated in isolation, with limited analytical capabilities.
The AI-Powered Healthcare Era (2015-Present)
The current era of AI in healthcare represents a fundamental shift from digitization to intelligentization. With advances in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, healthcare systems can now learn from data, identify patterns, and support clinical decision-making in ways previously unimaginable.
As Dr. Eric Topol, author of “Deep Medicine,” states: “AI has the potential to restore the care in healthcare by freeing up clinicians’ time, providing them with smarter systems, and making medicine less expensive and more accurate.” This shift is what makes the current transformation in AI in healthcare fundamentally different from previous technological upgrades.
Part 2: Key Concepts Defined
Understanding AI in healthcare requires familiarity with several key concepts and technologies:
Medical AI
The application of artificial intelligence technologies to medical diagnosis, treatment recommendations, patient monitoring, and healthcare management.
Machine Learning in Medicine
Algorithms that can learn from medical data to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks. This includes supervised learning for disease prediction and unsupervised learning for patient stratification.
Deep Learning for Healthcare
Advanced neural networks capable of processing complex medical data such as images, waveforms, and genetic sequences. These systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in areas like medical imaging analysis.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Clinical Text
AI systems that can understand, interpret, and generate human language from clinical notes, research papers, and patient communications.
Computer Vision in Medical Imaging
AI technologies that enable computers to interpret and analyze medical images from X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and pathology slides.
Predictive Analytics in Healthcare
The use of statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify future health outcomes based on historical and real-time data.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
AI-powered tools that provide clinicians with patient-specific assessments or recommendations to aid clinical decision-making.
Digital Therapeutics
Evidence-based therapeutic interventions driven by software to prevent, manage, or treat medical disorders.
Part 3: How It Works: Implementing AI in Healthcare (Step-by-Step)
The successful implementation of AI in healthcare follows a structured, evidence-based approach:
Step 1: Problem Identification and Use Case Selection
Begin by identifying specific healthcare challenges where AI can provide meaningful solutions:
- Conduct clinical workflow analysis
- Identify high-impact opportunities for AI intervention
- Assess data availability and quality
- Define measurable clinical and operational outcomes
Step 2: Data Acquisition and Preparation
Healthcare data requires careful handling and preparation:
- Aggregate data from EHRs, medical devices, and patient records
- Implement data anonymization and privacy protection
- Clean and standardize medical data
- Address missing values and data quality issues
- Ensure compliance with HIPAA and other regulations
According to our analysis of successful healthcare AI implementations, organizations that invest in robust data governance achieve 60% better model performance and faster regulatory approval.
Step 3: Model Development and Validation
Develop and rigorously validate AI models:
- Select appropriate algorithms for clinical applications
- Train models on diverse, representative datasets
- Implement cross-validation techniques
- Conduct clinical validation studies
- Establish model performance benchmarks
Step 4: Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Review
Navigate the complex regulatory landscape:
- Prepare FDA submission documents for software as medical device (SaMD)
- Conduct ethical reviews and bias assessments
- Implement explainability and transparency features
- Establish ongoing monitoring and update protocols
Step 5: Clinical Integration and Workflow Design
Integrate AI solutions into clinical practice:
- Design user-friendly interfaces for healthcare professionals
- Integrate with existing clinical systems and EHRs
- Develop clinical protocols and guidelines
- Train healthcare staff on AI system usage
Step 6: Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Ensure ongoing performance and safety:
- Implement real-time performance monitoring
- Establish feedback mechanisms from clinicians
- Schedule regular model updates and retraining
- Monitor for concept drift and performance degradation
As highlighted in The Daily Explainer’s guide to clinical AI implementation, healthcare organizations that follow structured implementation frameworks see 45% higher adoption rates and better patient outcomes.
Part 4: Why It’s Important – The Impact of AI on Healthcare Delivery
The significance of AI in healthcare extends across multiple dimensions of medical practice and patient care:
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
AI systems are revolutionizing medical diagnosis through:
- Radiology image analysis with sub-millimeter precision
- Pathology slide analysis detecting rare cellular patterns
- Early detection of diseases from medical scans
- Reduced diagnostic errors and variability
Studies show that AI systems can detect certain conditions like breast cancer from mammograms with accuracy rates exceeding human radiologists, as documented in Nature’s research on AI diagnostics.
2. Personalized Treatment Planning
AI enables truly personalized medicine through:
- Genomic analysis for targeted therapies
- Prediction of individual drug responses
- Customized treatment recommendations
- Dynamic adjustment of treatment plans
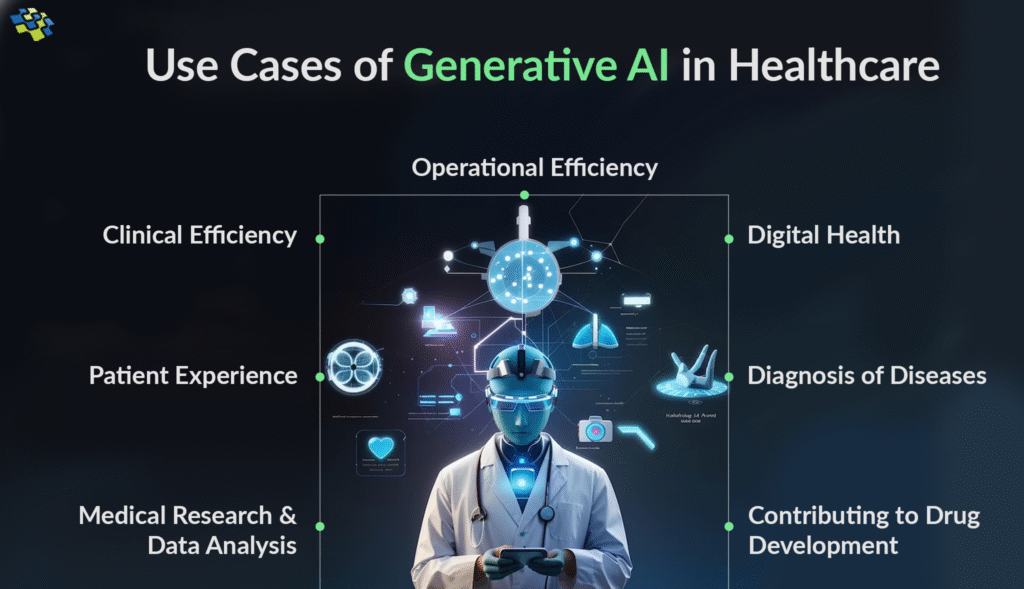
3. Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Healthcare organizations are using AI to optimize operations:
- Automated administrative tasks
- Optimized staff scheduling and resource allocation
- Predictive maintenance of medical equipment
- Reduced hospital readmission rates
4. Drug Discovery and Development
AI is accelerating pharmaceutical research through:
- Virtual screening of compound libraries
- Prediction of drug-target interactions
- Optimization of clinical trial designs
- Identification of drug repurposing opportunities
5. Remote Patient Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
AI-powered systems enable continuous care through:
- Real-time analysis of wearable device data
- Early warning systems for patient deterioration
- Personalized lifestyle recommendations
- Automated medication adherence monitoring
6. Medical Research and Knowledge Discovery
AI is transforming medical research by:
- Analyzing vast scientific literature
- Identifying new disease patterns and correlations
- Accelerating genomic research
- Facilitating collaborative research networks
Part 5: Common Misconceptions About AI in Healthcare
Several myths and misunderstandings often hinder the adoption and effective implementation of healthcare AI:
Misconception 1: “AI Will Replace Doctors and Healthcare Professionals”
Reality: AI is designed to augment, not replace, healthcare professionals. These systems handle repetitive tasks and data analysis, allowing clinicians to focus on complex decision-making and patient interaction.
Misconception 2: “AI in Healthcare is Only for Large Medical Centers”
Reality: Cloud-based AI solutions and AI-as-a-Service models are making advanced healthcare AI accessible to smaller clinics and rural healthcare facilities.
Misconception 3: “AI Systems are Black Boxes That Can’t Be Trusted”
Reality: Advances in explainable AI (XAI) are creating transparent systems that can provide reasoning for their recommendations, building trust with healthcare providers.
Misconception 4: “Implementing AI Requires Complete System Overhaul”
Reality: Many AI solutions integrate with existing healthcare infrastructure through APIs and interoperability standards, minimizing disruption to current workflows.
Misconception 5: “AI in Healthcare is Mainly for Diagnosis”
Reality: AI applications span the entire healthcare continuum, from prevention and early detection to treatment, monitoring, and follow-up care.
Part 6: Recent Developments in AI Healthcare
The field of AI in healthcare is advancing rapidly, with several groundbreaking developments:
1. Generative AI for Clinical Documentation
The emergence of large language models is transforming clinical administration:
- Automated medical note generation
- Clinical correspondence drafting
- Patient education material creation
- Research paper summarization
According to recent studies highlighted by The New England Journal of Medicine, AI-assisted documentation can reduce administrative burden by up to 50%, allowing more time for patient care.
2. Federated Learning for Healthcare AI
New approaches to model training that preserve privacy:
- Multi-institutional model training without data sharing
- Improved model generalizability across populations
- Enhanced data security and privacy protection
- Collaborative research while maintaining data sovereignty
3. AI-Powered Surgical Systems
Advanced robotics and AI are transforming surgery:
- Real-time surgical guidance systems
- Predictive analytics for surgical outcomes
- Automated surgical video analysis
- Enhanced precision in minimally invasive procedures
4. Digital Twins in Healthcare
Virtual replicas of patients and organs enable:
- Personalized treatment simulation
- Surgical procedure planning and practice
- Drug response prediction at individual level
- Disease progression modeling
5. AI for Mental Health
Growing applications in psychological care:
- Emotion recognition from speech and text
- Personalized therapy recommendations
- Early detection of mental health conditions
- Continuous mental health monitoring
6. Regulatory Framework Evolution
Governments worldwide are developing specific guidelines for healthcare AI:
- FDA’s Digital Health Center of Excellence
- EU’s Medical Device Regulation updates
- Specific guidelines for algorithm transparency
- Standards for continuous learning systems
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
AI in healthcare represents a fundamental transformation in how we prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases. It’s moving from experimental applications to essential tools that enhance every aspect of healthcare delivery.
Key Takeaways:
- Augmentation, Not Replacement: The most successful implementations of AI in healthcare enhance human expertise rather than replace it, creating powerful collaborations between clinicians and algorithms.
- Data Quality is Foundation: The effectiveness of healthcare AI depends entirely on the quality, diversity, and representativeness of the training data. Robust data governance is non-negotiable.
- Clinical Integration is Crucial: Technology must be designed around clinical workflows and user needs. Seamless integration into existing systems and processes determines adoption success.
- Ethical Implementation is Essential: Healthcare AI requires careful attention to bias mitigation, explainability, privacy protection, and ongoing monitoring to ensure patient safety and trust.
- Regulatory Compliance is Complex: Navigating the regulatory landscape requires careful planning and expertise, particularly for AI systems classified as medical devices.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Healthcare AI systems must be designed for ongoing monitoring, validation, and improvement to maintain performance and adapt to new clinical knowledge.
- Patient-Centered Design: Ultimately, all healthcare AI should serve patient needs—improving outcomes, enhancing experiences, and increasing accessibility of quality care.
The journey of integrating AI in healthcare is just beginning. The technologies and applications we see today represent the foundation of a much larger transformation that will continue to evolve. Healthcare organizations that embrace this transformation with strategic vision, clinical partnership, and ethical commitment will lead the way in creating the future of medicine—a future where AI-powered healthcare is more precise, personalized, and accessible to all.
For more insights on implementing AI in healthcare settings, explore our comprehensive healthcare AI strategy guide and stay updated with the latest developments in medical AI innovation.




1 thought on “AI in Healthcare: The Complete Revolution in Medical Practice and Patient Care”